YEAR OF SMALL LANGUAGE MODELS

The AI infra will pick up a lot of steam and revenue in Small Language Models (SLMs) as compared to LLMs. If LLMs are all knowing omnipotent gods, the SLMs are genie in portable lamps. The requirement of enterprises is task based AI, ie evolving systems with world knowledge of specific topics with low latency and cost. SLMs fits this bill perfectly. Most of the SLM development will be inhouse by ML wizards as the top brass wants higher intelligence embedded into applications that can be relied on. This is why it makes such a strong case for infrastructure play, that too open source. Infrastructure from data annotation, to RL environments, to eval benchmarking and evolving schema. Everything except the models themselves are a great place to build in this niche.
Many startups will realise that building software is easy, but building models is hard. The models require propietary data and architechture of ML models still fundamentally complex. Thus it would be great grounds to compete on. We will see a lot of demand for infrastructure around building these models
multiple better pytorches would be my first 2026 bet.
AI SOCIAL MEDIA (consumer AI)

Every AI startup which has decent traction will start running around circles, desparately wanting a moat - largely to raise money, and if the founders are somewhat decent then to also defend their business long term. The moat thats' being predicted is deep personalisation of AI models, social status being driven using AI content and marketplaces (More on marketplaces later). I want to focus on AI and social status, because there could be some market forming especially after niche adoption of Veo and Sora.
We will start seeing cracks in social media finally. The long lasting bastion of the giants like Facebook, X and others might just show some gap for others to create a space in. (It is also great space for decentralised identity to show value). AI will allow easier engagement with Videos and Content. The below graph is my hypothesis of what an AI social media will look like as compared to facebook.
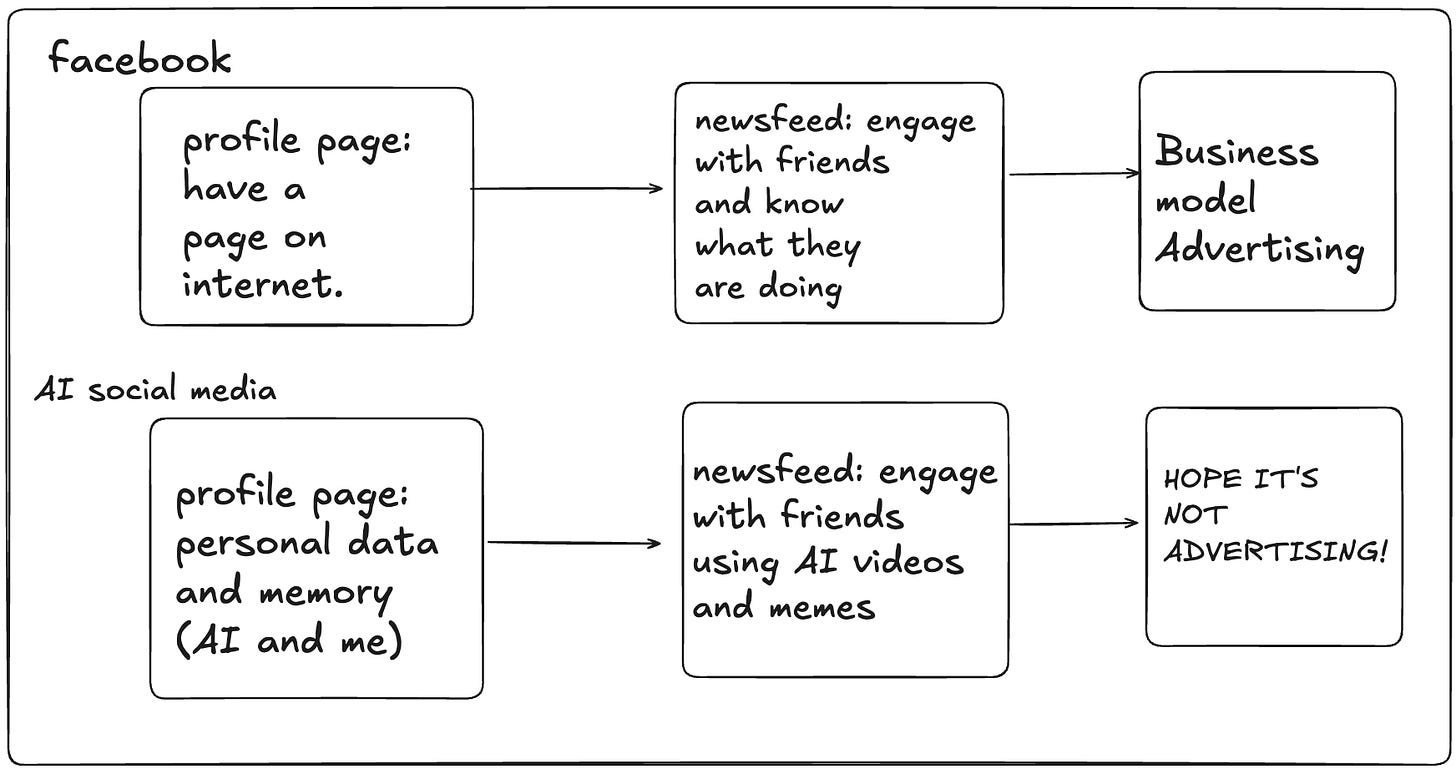
The reason why I am bullish on AI social media is because it can also help people with "what" to post and not just how to post it. Right now distribution channel do not personalise for an user and suggest what to respond / engage on as it would hated on intially. This makes it a great niche for a startup to build on.
DUMB NICHES

I think 2026 is the year we will see some dumb niches getting a lot of hype and traffic. There is a startup which works on figuring out how you can dream better, and also how you can better visualize, remember and enjoy your dreams. I always found it fascinating as most of my dreams ended post wetting my bed (figuratively and literally as well). Reddit Sub on Dream Interpreation has 93K subs
Another dumb startup I know built a yoga clapping productivity tool, which asks you to do different patterns of clapping yoga to be productive (again personalised to very specific WFH niche) but it got some revenue (perhaps more than 100th iteration of a vibecoding app).
It's harder to predict dumb niches but I am confident there will be many. AI curiosity especially among pro-sumers will be all time high which will lead to dumb niches exploding. Dumb things are easier to distribute as they are talked about more than serious things, so getting a high NPS is less of a challenge for super dumb ideas and super ambitious ideas.
MARKETPLACES

We have already seen glimpses of this when the vibecoding startups in bid the adieu more customers are advertising revenue. When agentic coding is solved problem, but niche community is not, we see rise of software marketplaces. [[This kind of boom and bust cycle was seen in crypto startups which at their base layer is a community of people who will simply not sell their tokens promising a base price for the token.]]
Marketplaces when linked to right demand and supply heuristic, can be trillion dollar economies. The best example for it is obviously content distribution and advertising. To be more particular about kind of marketplaces we will see in 2026, here are my best answers:
LLM applications (top LLMs - ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude) will come up with ways for external api / data providers to be listed, discovered, reviewed and paid as well and will give rise to LLM app marketplaces. Other LLMs will copy this model.
Cursor / Replit / Bolt / Lovable … will come up with app marketplaces for applications to be constrained and shared easily (vibecoded) that offer full control to the creators. It will be fueled by funding money to get the ball rolling initially, although the ball will be in the hands of creators more than developers.
I also think that builder x creator will be the most killer combination to posess. If you are an average builder - you should start your creator journey, and vice versa. The biggest oppurtunities will lie in the middle, and keeping up can help you monetize the small wins.
LESS APIGENTIC, MORE MCP

We saw investments in both horizontal and vertical agents in 2025, although personally I think it was too early to invest in horizontal / vertical agents. I would classify agents in three categories:
- chatbots with LLM APIs where distribution is owned by the startup
- chatbots where clients own the distribution, and agents are triggered (ex. MCP, Skills, ChatGPT apps)
- UI enabled interfaces with intelligence delivered by AI
I have been closely following the MCP UI, Registry development. I think clients will evolve in spending less tokens and choosing the right MCPs powered by registry, leading to rise of adoption of MCP / similar architechtures (ChatGPT apps / Claude Skills).
The "vertical" agents lying in first category will still be a hard sell, especially if they are an upteenth vertical agent, with no clear niche to grow out from. This is why less APIGentic agents and more agents with distribution network effects from the LLM Client.
I am also super bullish on interfaces agents. Agents that lie in interfaces, so if an agent is embedded inside an interface, they will see huge momentum, few examples we have seen already:
- Claude Code (Terminal Interface powered by AI)
- Cursor (VS Code powered by AI)
- RogerAI (Mobile Keyboards powered by AI) - (My Startup)
ONE COFFEE LATTE, OMELETTE AND AN AI BUBBLE PLEASE....

A lot of talk has happened about if we are an AI bubble. A lot of people with wads of money have been asked this question and have vehmently denied that we are in one. Bubble is always realised when they pop, till then they are economies. I don't think we are in an AI bubble yet. I think the federal reserve will find itself in predicament where it will lower interest rates to help the unemployment which in turn will lead to a small bubble by the end of 2026. If there was a thing I was least confident about in this list then it would be this (and yet make most money as well) would be the timing of gold rush in AI, but I am confident it will definitely happen by early 2028.
P.S I am building RogerAI









